Bladder Cancer
WHAT IS THE USUAL PRESENTATION FOR BLADDER TUMORS?
The commonest presentation for bladder tumors is bleed in the urine which is generally painless. However if a large volume of bleed occurs then the patient may have clot retention of the urine, which can be very painful.
HOW ARE SUPERFICIAL BLADDER TUMORS BEST DIAGNOSED?
Initial ultra-sonography is the best screening tool for bladder mass detection. However the gold standard for bladder mass detection is flexible cystoscopic evaluation of the patient. This procedure is performed on an outdoor basis. The procedure is done under local anesthesia. Since the patient is fully conscious he can see the procedure while having little or no pain, since the examining telescope is flexible.
WHAT IS THE MANAGEMENT FOR SUPERFICIAL BLADDER CANCERS?
The most common variety of bladder tumors are the superficial tumors. These are not invasive and therefore do not breach the bladder muscle wall. Therefore although these tumors can recur they do not change or reduce the life expectancy of the patient. These tumors generally are caused by habitual smoking.
WHAT IS TURBT?
Trans-urethral resection of bladder tumor or TURBT, is the gold standard treatment for superficial bladder tumors. This procedure is performed via the urine passage without the need to place any incision. The uro-surgeon using a resectoscope can visualize the tumor and resect the tumor using electrical or laser energy. Once the tumor is resected then the base of the tumor is sealed to control the chance for bleed. The patient is usually discharged after three days, and needs to take rest at home for 2 weeks after the procedure. This is essential since the bladder tumor resection wound heals completely in 2 weeks time, therefore the rest allows unhindered healing of the tumor scar.
WHAT IS THE PROGNOSIS AND FOLLOW UP FOR SUPERFICIAL BLADDER CANCERS ?
The prognosis of superficial bladder tumor management is excellent, provided the patient quits smoking completely. The patient leads a normal and healthy life with normal life expectancy. However the patient is maintained on follow up with periodic check cystoscopy. This procedure is performed at increasing interval of time, and since it is a painless day care procedure therefore the patients quality of life remains excellent.
WHAT ARE INVASIVE BLADDER CANCERS?
One out of ten bladder cancers can be aggressive and invasive. These tumors have the tendency to spread locally outside the bladder wall and also spread via the blood stream to distant organs like the liver and the lungs. This tumor has to be diagnosed by a transurethral bladder biopsy. Once diagnosed the tumor along with the affected bladder should be removed without further delay.
WHAT IS THE MANAGEMENT FOR INVASIVE BLADDER CANCERS, RADICAL CYSTO-PROSTATECTOMY?
Radical cysto-prostatectomy is the gold standard and till date the best curative option for the management of bladder tumors which are invasive in nature. This surgery performed by laparoscopy or by open surgical incision removes the entire bladder along with its enveloping fat, its drainage lymph nodes along with the prostate. After such a surgery the ureters are drained via an ileal conduit. This conduit drains the urine through a urostomy bag attached by adhesive to the lower part of the abdomen.
CONTINENT URINARY DIVERSION AFTER RADICAL CYSTOPROSTATECTOMY
After the bladder and the prostate has been removed in a case with advanced cancer of the bladder, the kidneys cannot drain the urine directly to outside the body via the penis.
In this case a new bladder can be created. This neobladder can be used to replace the cancer damaged older bladder. This bladder is created from the patient’s small intestine.
The surgeon harvests 70 cm of the intestine, this tubular structure is then de-tubularized to create a pouch. This pouch is then attached to the two ureters. (Ureters are the tube via which the kidneys drain the urine into the bladder)
The surgeon then attaches this bladder to the urethra, which is the tube which drains the urine via the penis in the male to outside the body.
This procedure is possible in organ confined cancer, wherein the cancer is removed and the patient is able to get a new bladder created replacing the older damaged bladder. He is also able to pass urine via the normal urine passage.
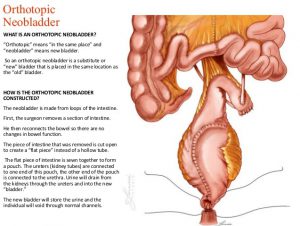
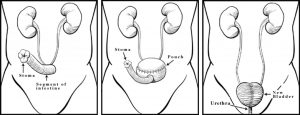
NEO BLADDER RECONSTRUCTION
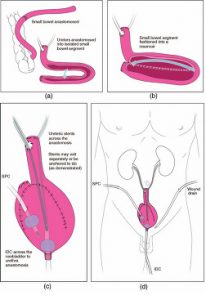
NEO BLADDER SUBSTITUTION
Bladder invasive cancer in females
Bladder cancer is more common in males. And has a direct correlation with smoking cigarettes and Bidi. However females can also be affected by this cancer.
When the cancer becomes invasive then there is a chance of spread to distant sites in the body and there is risk to life.
In these cases the best management is laparoscopic radical cystectomy. This sugery can cure these patients since the affected bladder along with the uterus and a cuff of the vagina is removed .
This surgery can nowadays be performed by laparoscopy wherein the patient has lesser invasion and therefore faster recovery. Laparoscopy means the organ removal is performed via five small ports (small incisions)
After removal of the bladder cancer we also create a new passage for passage of urine. We can create a new bladder in patients with early bladder cancers. This bladder is created from the patients own intestine. And patient can pass urine via the normal urine passage. However in advanced cancer we create a new passage called an ilial conduit for the urine to pass from a new opening created in the right lower part of the abdomen. A bag can be attached to this mouth so urine can be collected within this bag. Therefore bladder cancer even if life threatening, can be cured today by keyhole surgery.