
 NKPC has state of the art gastro-enterology and surgery clinic
NKPC has state of the art gastro-enterology and surgery clinic
Facilities at a glance
Gastroenterology
1.Olympus upper GI endoscope
2. Olympus lower GI endoscope
3. Olympus ERCP scope
4. state of the art operating theater with advanced instruments
5. harmonic scalpel
6. advanced bipolar for hemostatic control
7 . high definition camera for laparoscopic surgery
- 1288 stryker camera
- 1588 stryker camera
Faculty of gastro-enterology
- Dr S B Das Chakroborty MD DM Gastroenterology


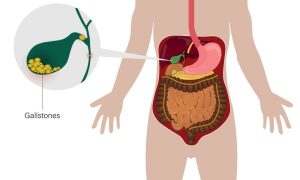
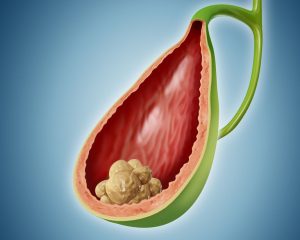
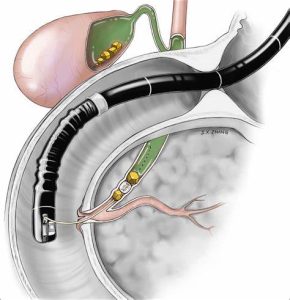
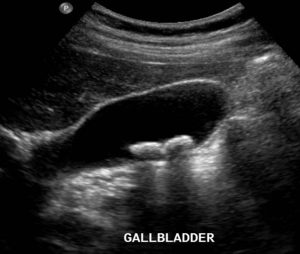 Gall stones are best detected by ultrasonography. This simple and painless test is very sensitive to detect gall stones and also assess the status of the common bile duct. We also will ask for routine liver function test and amylase lipase to assess the pancreatic function as well.
Gall stones are best detected by ultrasonography. This simple and painless test is very sensitive to detect gall stones and also assess the status of the common bile duct. We also will ask for routine liver function test and amylase lipase to assess the pancreatic function as well.

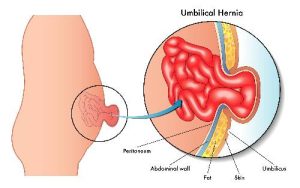
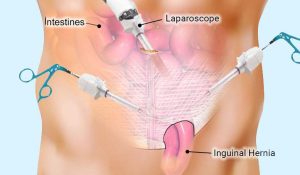
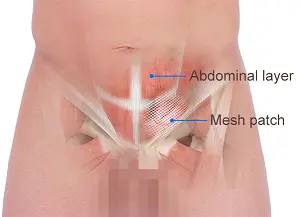 Since the muscle has a defect then we are able to fill the gap in the muscle by two techniques. Either we use a mesh, this is a synthetic cloth like material which is permanent in nature therefore it will permanently reinforce the gap in the muscle.
Since the muscle has a defect then we are able to fill the gap in the muscle by two techniques. Either we use a mesh, this is a synthetic cloth like material which is permanent in nature therefore it will permanently reinforce the gap in the muscle.